- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Adtran Support Community
- :
- Documentation
- :
- Enterprise-Class Wi-Fi
- :
- BlueSecure Controllers (BSC) - End of Life
- :
- BSC Best Practices and Common Troubleshooting Procedures
BSC Best Practices and Common Troubleshooting Procedures
BSC Best Practices and Common Troubleshooting Procedures
This article aims to present best practice guidelines for all ADTRAN BlueSecure Controller (BSC) models and document steps that can be used to troubleshoot common BSC issues. Please note this product line has been discontinued as of 31 December 2014. The product line will no longer be supported after 31 December 2015. All documentation on the ADTRAN Support Community will remain available.
Sections in this document
![]()
General Recommendations for Better Performance
Use the following suggestions to get the best performance out of the BSC platform. More detailed information, if available, can be found by clicking the entries.
- Check the BSC and BSAP (if applicable) software levels
- Compare the maximum supported users and APs to the actual number of users and APs on the BSC
- Remove obsolete local user (User Authentication > Local Users) and MAC device accounts (User Authen...
- Turn off the AP service for controllers that do not manage Bluesocket AP’s (Wireless > Service > uncheck “Enable AP Service”)
- Disable replication if there are no Replication Nodes
- On pages where multiple rows are shown (e.g., Active Connections, Logs, etc.), keep displayed rows to minimum whenever possible
- Keep firewall rules (Roles) as concise as possible
- Identify possible additions to the server block list
Make sure the BSC is running the latest software and patches, and check that the BlueSecure Access Points (BSAPs) are also running the latest available software compatible with the BSC platform. ADTRAN recommends the following software for BSC deployments.
- BSC software version 6.5.1.03
- Bluepatch 1 (Release One)
- BluepatchAddOn-Supplemental
- BluepatchAddOn-RemoteSubnetIp Range
- BSAP 6.5.4-10
The easiest way to find software is by following the links below.
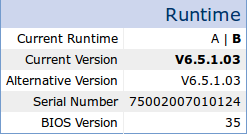
The BSC software can be confirmed under Maintenance > Upgrade. The BSC maintains two separate partitions. The current runtime (partition) and version are shown in bold.
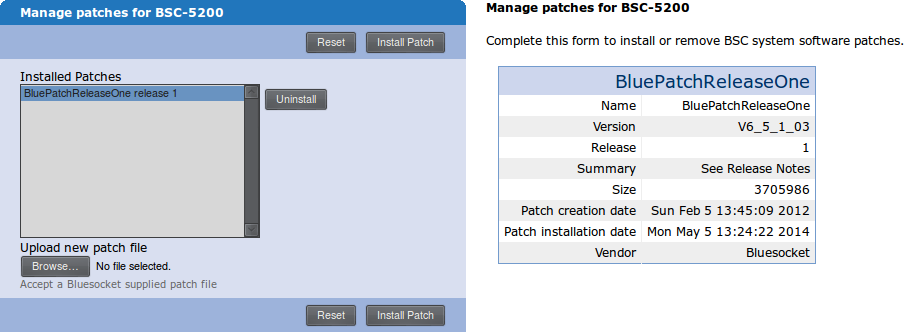
The installed patches are listed under Maintenance > Patch. There are two sections displayed on this page. The left-hand section lists all installed patches. Clicking on a patch will display details about that patch on the right-hand side.
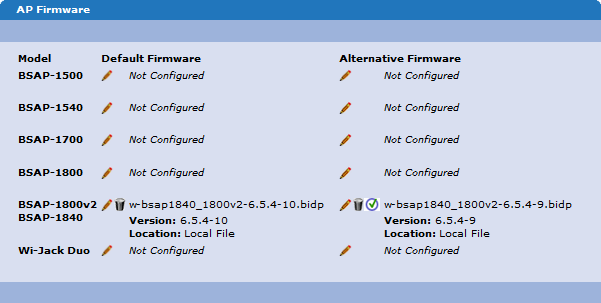
The BSAP software is located under Wireless > Firmware. A default and alternative firmware version is listed as shown in the image below. Any alternative version can be made the default by clicking the green check near the alternative firmware version.
Use the system summary (Status > Summary) to compare the Total Number of Users to the max supported for the model in question. Also compare the Total Number of Active Access Points to the max supported for the model in question. The following table is an abbreviation of the existing article How many concurrent authenticated users and BSAPs does each model BSC support?
Table 1. Max Supported Users and APs per BSC Model
| Model | Max Users | Max APS |
|---|---|---|
| BSC 600 | 64 | 8 |
| BSC 1200 | 200 | 25 |
| BSC 2200 | 400 | 50 |
| BSC 3200 | 1500 | 100 |
| BSC 5200 | 4000 | 150 |
It is important that the number of users and APs be less than the allowed maximum for the model as described above. Reduce the number of APs or users as needed. Reducing the number of users on a wireless system can sometimes be difficult. Implementing a password protected SSID is one option (Wireless > SSID). Reducing the number of APs or implementing a client limit per AP is another option. Client limits are global settings per radio (Wireless > Global) or per AP (Wireless > AP). This is different than simply deleting obsolete user accounts, which should also be done as a part of regular maintenance.
Local and guest users can be configured to expire automatically. If the accounts are not setup to expire or perhaps just did not expire when they were supposed to, then delete all obsolete or unused accounts. This cleanup should also include MAC Device Authentication entries that are not being used. Local, guest, and MAC devices authentication are found under the section of the BSC. Click the trashcan icon under the Actions column to delete an entry. Alternatively check multiple entries and click the Delete button located under the list.
If replication is not being used, then make sure that replication is disabled. Leaving replication enabled can lead to high CPU utilization when there are no replication nodes available. This can lead to new problems or exacerbate existing ones. When replication is disabled, the Mobility MatriX > Replication Setup page could indicate as much in bold.
The BSC solution utilizes role-based access control to enforce firewall policies on clients connected to the managed side. Roles are found under Roles > Roles. These policies are processed in a top-down fashion until a match is found or no more policies are present. This provides two options for optimization: place common ports at the top of the policy list and keep the policies as concise as possible. For example, DNS, HTTP, and HTTPS are the primary protocols used for typical internet access. If a policy is related to these protocols, then it should likely be at the top of the policy list.
The server_black_list is a file (Web Logins > File Uploads) used in the Un-registered role (walled garden). When an Un-registered client is being redirected to a captive portal, if the URL they are trying to access contains a term in the black list, then that redirect attempt will be dropped. This action uses significantly less CPU cycles, and therefore is a good way to reduce CPU overhead associated with captive portal authentication. For example, mobile devices often try to access a site hosted by the vendor or provider, and this happens as soon as an internet connection is enabled. Adding the vendor name to the black list means that these initial, uncontrolled requests will not burden the CPU as much as if those requests were redirected to the BSC. This is because actions based on the server black list happen prior to the web server needing to process the traffic.
BSC Upgrade and Patch Process
ADTRAN recommends that all BSCs run the latest available software as listed below.
- BSC software version 6.5.1.03
- Bluepatch1 (Release One)
- BluepatchAddOn-Supplemental
- BluepatchAddOn-RemoteSubnetIp Range
- BSAP software 6.5.4-10 for the BSC platform
The Software (BSC) section of the ADTRAN Support Community can be used to find the appropriate controller software. BSAP software is available by following the appropriate link under the Software (BSAP) section. BSC software and patches have two formats depending on the BSC model. The extension *.i386.bpf is used for the 2200/3200/5200 platforms while *.mips.bpf is used for the 600/1200 models. Follow the outline below after downloading the appropriate software.
- Perform a configuration backup (Maintenance > Configuration Backup/Restore > select Backup > click Save).
- Large systems may require adjusting the seconds a client is allowed to hold the web server. This is found under General > HTTP, and a temporary value of 300 seconds should be used. Applying this setting will require the web server to restart. The system will present a message in red text near the top of the interface with further instructions. After the backup is complete, reset the value back to its previous value (recommended 10 seconds).
- (Required for BSCs operating using Replication) Browse to Mobility MatriX > Replication Setup and uncheck the replication node or master option, then click Save. Follow any messages presented to apply these changes.
- (Required for BSCs not running 6.5.1.03) Browse to Maintenance > Upgrade, select Maintain Current Configuration if applicable, click Browse to load the BSC software image file, then click Upgrade to start the upgrade process.
- A reboot will be required after the upgrade is complete.
- (Required for BSCs not running the recommended patches) This step requires that the BSC is already running 6.5.1.03. Browse to Maintenance > Patch, click Browse to load the patch(es). After installing each individual patch, follow the instructions presented by the BSC, including reboots if necessary. Patches should be installed in the following order.
- Bluepatch1 (Release One)
- BluepatchAddOn-Supplemental
- BluepatchAddOn-RemoteSubnetIp Range
- (Required if BSAP software is not 6.5.4-10) AP firmware is listed under Wireless > Firmware. Click the pencil icon next to the appropriate model AP to load new AP firmware.
- On the edit screen, click Browse to select the file, then click Save to make the change.
- Follow these instructionsif presented with a 20MB space error when uploading new firmware.
- (Optional) Back on the main firmware page, click the green check to change alternative firmware to default firmware.
- Follow any notifications from the BSC to apply the new AP firmware.
- On the edit screen, click Browse to select the file, then click Save to make the change.
Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting Steps
Start by making sure to follow the best practices above. Try to eliminate unnecessarily high client counts as reducing the number of clients will alleviate most CPU and webserver related problems. Next, note the following information on the summary page.
- CPU Usage. If this is consistently over 70% or often spikes, then proceed to the section CPU Utilization is High
- Memory Usage. If memory usage is consistently high, then it may be necessary to reduce the number of clients on the system.
- Disk Usage (Current Partition). If it is over 90%, then check for login items (Web Logins > File Uploads) and delete any unnecessary files or delete unused alternate AP firmwares.
- Check Log Space Usage (Current Partition). If issues are around logging, then try to purge log files (Status > Logs) or proceed to Logging Issues section.
Using the information above and any other problem description, proceed to the applicable sections below. If the steps in the other sections did not resolve the issue, then reboot the equipment under Maintenance > Restart Services > select Reboot > click Submit. If the administrative portal is not available, then use a console cable to access the serial console menu.
CPU Utilization is High
There are two primary causes of high CPU utilization: user count and logging. Make sure user and AP totals are within allowed range of the BSC model. Table 1 above provides these numbers or check How many concurrent authenticated users and BSAPs does each model BSC support?. If users are over 90% of the total allowed, it can still cause high CPU numbers. If open SSIDs are present (Wireless > SSID), then try switching to an authentication mechanism that still fits the needs of the application. ADTRAN recommends at least WPA2-PSK/AES.
If the user count is within the acceptable limits for the BSC model in question, then check logging levels and lower any debug-level settings under General > Logging. Try to identify any roles that could be trimmed. Follow the directions in the next section to eliminate some web server traffic, if applicable.
Identifying Undesired Redirection Traffic (for blacklisting)
Redirecting traffic associated with captive portal authentication is one of the main culprits for high CPU utilization on the BSC platforms. When suspect traffic occurs, or a difference in performance is noted, go to General > Logging and set User Tracking to Debug level. Note that additional performance impacts may be felt while the logging levels are set like this. These logging settings should only be temporary. Give the BSC some time to build up log entries, then download the logs under Status > Logs and open them for review. The message column can be used to identify the undesired traffic. Look for redirect messages.
Items can be added to the blacklist file so that all traffic attempting to contact a URL containing the keyword in the blacklist will simply be dropped, not redirected if the user is in the Un-registered role. The black list file itself is found under Web Logins > File Uploads, however, the file may not be shown if it has been removed or does not exist. If the file exists, then download it and open it in a simple text editor. If the file does not exist, then create a new file in a text editor, and save it as server_black_list. If additional keywords are added to the blacklist, save the file with the name server_black_list. Upload the server_black_list file to the BSC under Web Logins > File Uploads. Restart the web server under Maintenance > Restart Services > Advanced.
Logging Issues
Check the Log Space Usage (Current Partition) under System > Summary. If Log Space Usage (Current Partition) is over 90%, then consider purging logs under System > Logs. Reset or adjust logging levels under General > Logging. Disable all debug-level logging, and only enable debug-level logging when necessary. Monitoring processes requires the BSC Processes log level be set to at least Info level. Disable “Connection Tracking” or increase the interval (default: 120). Connection tracking sends a record of all network connections to syslog which can result in a large number of log messages and impact BSC performance. Only use if all network connection information needs to be logged for auditing purposes. Consider exporting logs to a remote syslog server. Generally avoid increasing the maximum number of log entries to store in the local database. If the max value is already set, then lower the number of logs to keep, or increase the number of log entries to delete when reaching the maximum.
Reports are Failing
If graphs do not appear properly or the report contains no data, ensure the Start Date and End Date are accurate. Make sure the end date is not before the start date and the years are correct. Verify there actually is data under Status > Logs. A lot of times that data is empty because the logs have already rolled off of the BSC. For example, a report is needed for the last 30 days of logs, but Status > Logs has the last 5 days. In this case, the BSC will display an error.
Web Server Fails to load or General Sluggishness
There are a few settings which can help improve responsiveness of the web server. The comma separated list of HTTP/proxy ports to monitor (General > HTTP) should only include port 80. Remove 443 if it is in the list. Make sure Denial-of-Service Evasion Options (General > HTTP) are set to a reasonable value. Use the recommended settings as guidelines.
- Seconds a client is allowed to hold the web server: 10 seconds
- Times per second a client can access a specific page: 2
- Times per second a client can access a specific host: 4
These recommended values work for most deployments. Custom login forms with lots of images may take longer to load. In those cases, increase the seconds a client is allowed to hold the webserver to a maximum of 30 seconds. The other values should rarely increase.
Sometimes clients may not redirect to the Web Page served on the BSC. Before a client is authenticated they are placed in the Un-Registered role. By default the Un-Registered role only allows DNS outgoing therefore the browser is unable to check the validity of the certificate and doesn't redirect to the login page. Upon redirection, the client’s browser uses OCSPs and CRLs to check the validity of the Web Server certificate. The default behavior of many of the browsers today is if they cannot check the validity of the SSL certificate they consider it invalid. The unfortunate thing is the browser does not display a message or anything to indicate it could not validate the certificate, it simply just doesn't display a page or displays a generic page cannot be displayed message. To find the OCSPs and CRLs, go to Web Logins > SSL Certificate on the right hand side and see the properties of your certificate. There you should see the OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol) or CRL (Certificate Revocation List) URLs. You may see one or both depending on the certificate. The 6.5.1.03 release introduced Destination Hostnames to account for the multiple IP addresses that may resolve from a host name. Once you have the OSCP and CRL URLs, you need to create Destination Hostnames (User Roles > Destinations > Create Destination Hostname) for each URL. Next, navigate to User Roles > Roles and click to edit the Un-Registered Role and allow HTTP access to the Destination Hostnames of the OCSP and CRL URLs.
Useful Links
-
 Anonymous
Anonymous