n-Command MSP Deployment Considerations and Best Practices
n-Command MSP (Managed Service Provider) is a sophisticated and continually evolving centralized platform for managing up to 25,000 AOS unit's configuration files, firmware, and device alerts as well as keeping a database of configuration backups and other critical data from each unit. This document covers deployment considerations and best practices for the n-Command MSP product in order to keep the server running efficiently and to ensure proper AOS device communication with the server.
Sections Included in this Document
Hardware and Software Requirements
General Deployment Considerations
- Licensing n-Command MSP
- User Accounts and Admin Dashboard
- Time Server Settings
- Network Settings
- Adding Static Routes
- DNS Configuration and Automatic Updates
- Automated Backups
- Server Alerts
- Unit Check-in intervals
- I-Drac Configuration for Dell Servers
- Advanced Issues and Technical Support
- n-Command MSP Help Page
Hardware and Software Requirements
An n-Command MSP server can be deployed on any version of firmware. However, it is recommended that the server be running the most current version of firmware to properly utilize all the current features and efficiency mechanisms. If utilizing the VMware version of n-Command, an OVA file must be used. While this may provision a lower version of firmware than the current RPM file, once the server is active you can upgrade to the most current version.
All of the information in this document is based on MSP version 7.X.X.
General Deployment Considerations
An n-Command MSP server requires a valid license and special provisioning to work properly. Along with this, n-Command MSP requires basic network settings to function correctly. Among these are network settings, User management, NTP Time server settings, and security for the server itself. The following section describes the need for each of these as well as an ADTRAN recommendation as to how to properly configure settings for proper server use.
n-Command MSP requires a license to function normally. Without a valid license, n-Command MSP will not accept connection request from new AOS units, will not upgrade to newer firmware versions, and will not be eligible for technical support. To obtain a license or to renew a license for your existing n-Command MSP server, email ncommandadmin@adtran.com for a quote. All licenses are 1 year in duration.
Once a License has been purchased, follow the licensing procedure on page 2 of the n-Command MSP Quick Start Guide to complete the licensing of the server. To properly license the server, the server's serial number must be registered to your account on www.adtran.com.
Note: You must have the server's serial number registered to the account you are logging in with. If it is registered to another individual at your business, while you will still be able to view the server registration, they will still need to log into their account to license the server.
n-Command MSP can modify the firmware, configuration, or even reboot any connected device, so access to the server itself should be managed securely. n-Command MSP allows four different types of user authentication methods: Local database, Radius, LDAP, and Active Directory. Though the other methods can be configured to properly allow the correct subset of users, ADTRAN recommends using the Local Database option for ease of configuration as well as limiting the number of users able to access the server without the need for external configuration. Local Database authentication is the only method covered in this document.
An n-Command MSP server ships with a default user account named "admin". This account can not be deleted and is hard coded with the highest permissions. A new user account can be created by clicking the Open Tab drop down menu and then clicking User Management. Inside, clicking Add a user allows a user account to be created (assuming the current user has user management permissions). On the resulting screen, there are check-box options on the right to limit the permissions for the created user. It is recommended these permissions are properly managed based on each individual user account. From the n-Command MSP UI, a user with full permissions can make massive changes to any network of AOS devices as well as the server itself.
In MSP 6.1.1, a new user management platform was created on the n-Command MSP server called the "admin dashboard". This view uses a separate user account that is not view-able from the main MSP UI. All of the critical server management functions like NTP settings, network configuration, Server Monitoring widgets, etc. are contained in this view. This dashboard can be accessed by adding "/msp" to the URL of the n-Command MSP server ( <n-Command MSP server IP address or domain name>/msp ). By default, the username is "admin" and the password is the n-Command MSP server's serial number (case sensitive). The password can be changed by going to settings->Change Password once inside. This does not affect the admin account in the normal UI.
The detachment of these functions into a separate UI view has allowed server admins a way to protect critical server functions from other users while still allowing desired users full permissions in terms of server function. The admin dashboard also runs on a separate HTTP daemon than the MSP UI. If for some reason the MSP server UI is unresponsive, the admin dashboard may still respond which can allow network settings to be checked. The UI and server itself can also be restarted from the admin dashboard by going to settings->Server Restart.
The below sections cover the critical settings in the admin dashboard that should be addressed in every server:
n-Command MSP can manage a multitude of AOS units through a substantial Postgres Database. All of the information, actions, and configuration of the units that it manages are stored in this database. A critical function in that database is time as data is cataloged based on timestamps. AOS units connected to MSP must match the MSP server's time and timezone setting to properly communicate configuration and firmware information as well as other features that inter-op with an MSP server. Because of this, it is recommended that n-Command MSP as well as all of the devices it manages are configured to use the same NTP time server and that this time server has redundancy and minimal downtime.
Note: Having time improperly configured on the n-Command MSP server or on a connected AOS device will often cause VQM records from that AOS device to not be displayed properly.
In the admin dashboard, the network settings can be changed by navigating to Settings->Network Settings. A physical n-Command MSP server includes two interfaces that can be configured for device contact or server management. In common cases, one interface will be configured with a public IP for Public management or device access and the second interface will be configured with a private IP for private management and device access. Configuring both interfaces is not a requirement. If using both interfaces, remember to properly set the default gateway so that it points out the interface most devices will be accessing the server through. Static routes can be added to the server for more robust and granular access as discussed in the following section.
In MSP version 6.1, the ability to configure static routes was added. To do this, navigate to settings->Static Routes and add the appropriate routes in. If you are on a prior version of n-Command MSP and wish to add static routes, you will need to upgrade the server to take advantage of the feature.
It is highly recommended a DNS server be configured in the n-Command MSP server admin dashboard. When a unit checks-in, it will perform reverse DNS lookup to locate a possible hostname for the unit's IP address. This process normally assures efficient server operation.
Along with this, n-Command MSP automatically checks into an ADTRAN Repository for firmware updates and as of MSP version 8.1.1, security updates as well. If it detects a new update, it will automatically download the update and wait for an admin to apply it. This is important as some updates could be critical in nature and may need to be applied post haste.
Note: Only a user with access to the admin dashboard has the ability to apply firmware or security updates.
n-Command MSP, while having some local inherent security settings, is not a firewall nor has a network firewall built into it. In most deployments, the server may need a public IP address as it will need to be accessed publicly by AOS devices or server admins. Failing to properly protect the server from outside threats can possibly lead to the server being compromised which could potentially compromise all connected AOS devices as well.
ADTRAN recommends that the server be deployed behind a firewall with either a static 1:1 NAT or NAT destination (Port Forward) firewall configuration or in a De-materialized Zone (DMZ) that only allows the required ports (covered below) to access the n-Command server. In either configuration it is recommended that access to the required open ports be restricted via Network address. ADTRAN also recommends that HTTP access to the UI on the configured port on a public interface is disallowed by the firewall.
ADTRAN recommends, especially if the server is deployed with a public interface, that the passwords used for user accounts are strong passwords and are not the same used on each of the network devices. Do not share passwords and accounts if possible and only grant access to the server to individuals that legitimately require access. Failure to restrict this properly can result in server and AOS unit downtime.
The n-Command MSP Quick Start Guide covers all ports that must be open based on the services that you are utilizing. Note that VQM is sent via TCP port 5060 on AOS NetVanta series routers, while sent over UDP 5060 on Total Access 900 and NetVanta 6000 Series IP Business Gateway Products. These ports must be properly opened for these services to function properly.
As of MSP version 6.1.3, TCP 8443 is used for configuration and file backups instead of the associated unit check-in port. This port must be properly opened/forwarded to MSP through a firewall or loss of server responsiveness may occur.
Command Line Interface (CLI) access to n-Command MSP, though running on CentOS is not accessible to customers. n-Command MSP is considered an appliance and therefor has all root and user CLI access locked down with no exceptions. For questions on this please contact ADTRAN Technical Support.
n-Command MSP can manage up to 25000 devices with a considerably large Postgres database. In order to efficiently perform thousands of operations a day on that database, server efficiency and maintenance are critical. If proper settings, maintenance, and backup settings are ignored, the server may become unresponsive as the database jobs become congested. The following sections discuss the critical settings and steps an admin must comply with to keep the server running smoothly.
Backing up the MSP server database is a critical function. If the server's database becomes congested or corrupted, rolling back to a prior point (while rare) can be necessary to keep from loss of data (backups, firmware, VQM and Pcash data, etc.). Under Settings->System Backups in the UI, a user can view system backups and create a schedule for backing the server up in the tab named Schedule Settings. ADTRAN Recommends the server be backed up once a night. Backups are stored locally on the server's hard drive by default. A remote server can be set up in the third tab named Remote Settings if desired to backup the database to a remote FTP server.
At this time, to rollback to a prior database file, it is necessary to contact ADTRAN Technical Support.
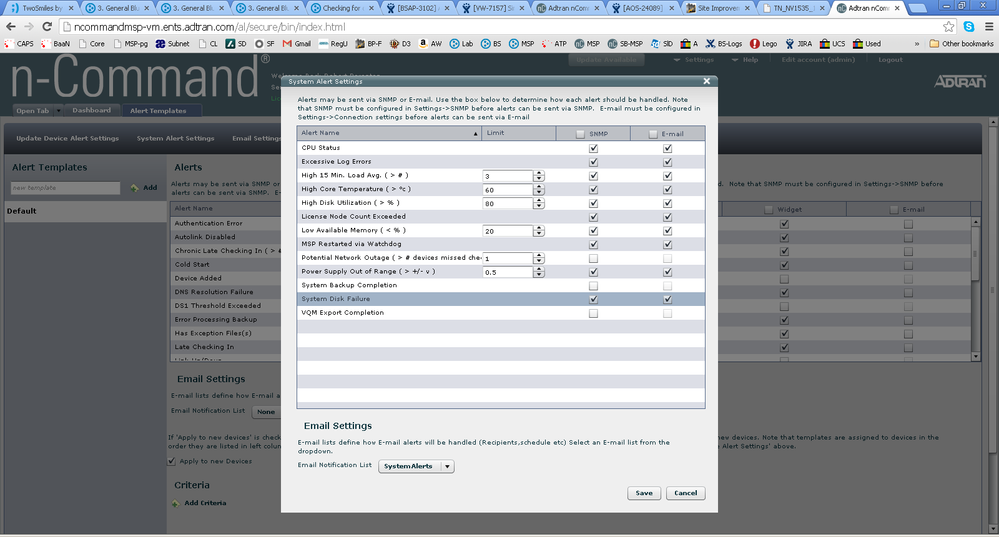
On the n-Command MSP home page, clicking on "Open Tab"->"Alert Templates will open the alert templates page. This controls all the alerts that MSP generates based on data it receives from each unit. When a unit checks in for the first time, it will automatically have the default template applied to the unit. These alerts can be viewed on the main dashboard, via E-mail, and via SNMP. The default template is recommended, but further granularity per unit can be configured from here.
At the top of the page, there is a section labeled "Server Alerts". Selecting this will show the below options:
It is highly recommended that these be set up with values that fit your organization's notification policies. Server specific alerts including those related to memory, disk utilization and failure, High CPU, and high core temperature should be sent in a manner that can be acted upon as quickly as possible as these could mean serious issues with the server itself or the underlying hardware. Generally these alerts should be sent to a different recipient (or acted upon in a different manner when received) than normal unit alerts as this can cause service issues with the entire MSP server.
The "Network Outage" alert can also be very useful. It can be set so that if a specific number of devices miss their check-in, it will alert of a potential network outage. This should be set up to a number of units that makes sense in relation to the number of units on the server. The default is 1, but on a server that has 10000 units checking in, this would need to be adjusted to an acceptable value.
When auto-link is configured on a device, the default auto-link recontact interval is 3600 seconds as referenced by the AOS command auto-link recontact-interval 3600 command, which is in the AOS auto-link configuration by default. It is recommended that this setting never be configured to a value less than 3600 seconds, especially across multiple devices. Configuring the recontact interval to a lower value adds load to the n-Command server and can cause disruption in vital processes like backups which may take time based on connection speed and disk write speed.
While it may be desirable to configure lower check-in intervals to more quickly confirm whether a unit is live or not, it should be understood that the check-in mechanism is not a monitoring capability. There are many server-critical processes that take place when a unit checks in. If these are interrupted or delayed because of check-in times that are too frequent, the server will eventually start to become overwhelmed and loss of management access could be possible.
In certain cases, if check-in times are low and server problems are persisting, ADTRAN Technical Support may require you change these before the server can be serviced.
If a physical n-Command server is purchased, it will either be a Dell 300 or Dell 600 physical server model. These servers come with an extra physical Ethernet port labeled Idrac. This port acts similar to a virtual console. Using the Dell Idrac configuration, console access can be gained to the server even if IP connectivity to the main server interface, or the UI is lost. It is recommended that this port be provisioned into your management network and setup with a few quicksteps before hand. This can be quickly utilized in the event of a server malfunction to regain service.
For information on setting up the Idrac port, please see the Idrac User Guide.
n-Command MSP is an appliance and therefor the underlying operating system and processes are not visible to a user. If issues occur that can not be resolved or troubleshot using the built in n-Command MSP UI tools, a user needs to open a ticket with ADTRAN Technical Support.
To quickly resolve issues with n-Command, ADTRAN Technical Support may require direct access SSH access to the server from ADTRAN. This can be done via a pre-installed VPN or a port-forward firewall rule. For quick resolution of issues it is recommended you have this set up and ready prior to calling support so that the server can be accessed and maintenance can be performed in a timely manner. Though shared sessions may be used in some cases, direct access will be required for most invasive troubleshooting.
For quick help with questions while logged into the n-Command UI, click on the "help" tab on the right-hand top of the page and click "Online Support" as shown below:
This will open up a new tab/window in your browser to a help wiki for n-Command MSP with information about all the major features and processes for the particular release you are currently using.